BDD is characterized by the obsessive idea that one or more body parts are repulsive, while these flaws are usually unnoticeable by others. These obsessive thoughts are often accompanied by depressive symptoms. Currently, the treatment options for BDD are antidepressants and cognitive behavioral therapy. Since many patients show insufficient response to these options, new treatment modalities are urgently needed.
Non-invasive brain stimulation
Under supervision of Psychiatrist Karel Scheepstra and Nienke Vulink, Neuteboom and van Paridon treated five BDD patients with a form of brain stimulation which does not require surgery or implantation of electrodes, called repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS). This treatment is already proven effective in patients who suffer from depressive symptoms but has never been assessed in patients with BDD. In this study, rTMS was applied according to a depression protocol to find out if the treatment could potentially alleviate both BDD and depressive symptoms.
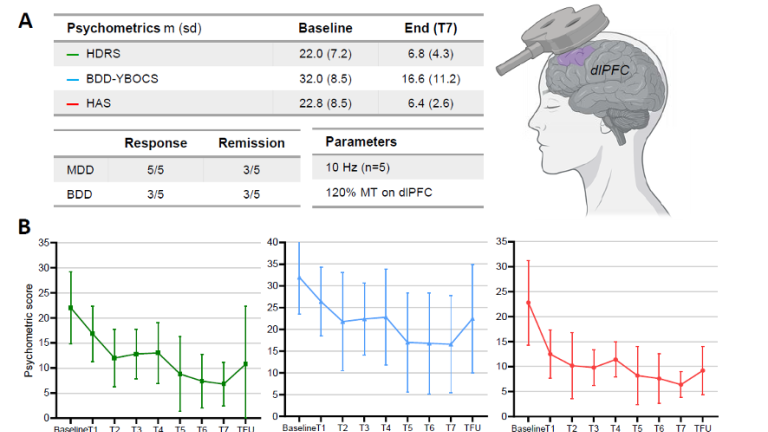
Positive effects shown in five patients
In this first study on rTMS in BDD patients, the effects are positive. All five patients had significant reduction of depressive symptoms and three out of five patients had a significant reduction of their BDD symptoms. Furthermore, the rTMS was tolerated well and no severe side-effects were seen. As a result of the positive effects in this small number of patients, a larger sham controlled study is currently being performed at Amsterdam UMC, location AMC, to study the efficacy of rTMS in BDD on a larger scale.

